797 Lakh MT of packaging waste was generated by European Union in 2023.

EU-PPWR is a Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation by European Union published on 19th December 2024. It came into force on 11th February 2025 and will be applicable from 12th August 2026.
What is EU-PPWR?
EU-PPWR is a Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation introduced by European Union to tackle the growing problem of packaging waste and drive the transition towards a truly circular economy.
It establishes requirements covering the entire lifecycle of packaging, focusing on environmental sustainability, labelling, extended producer responsibility (EPR), waste prevention, and waste management.
Purpose of EU-PPWR:
- Circular Economy Transition: To contribute to the transition to a circular economy and help the EU achieve climate neutrality by 2050.
- Waste Reduction and Prevention: To minimize the overall quantities of packaging and packaging waste generated and decrease the use of primary raw materials.
- Safety and Sustainability: To minimize the use of harmful substances in the packaging and to ensure that all packaging is reusable or recyclable by 2030.
What qualifies as packaging under EU-PPWR?
Packaging material includes any item that is used for the containment, protection, handling, delivery, or presentation of products regardless of its material composition.
Products covered under EU-PPWR:

Packaging is broadly defined and includes :
- Sales packaging : Primary packaging, for end users at the point of sale.
- Grouped packaging : Secondary packaging, grouping several sales units.
- Transport packaging : Tertiary packaging, facilitating handling and transport, excluding road, rail, ship, and air containers.
- E-commerce packaging : Transport packaging for online sales deliveries.
- Service packaging : Specific items like disposable plates/cups intended to be filled at the point of sale and single-serve units for beverages.
Who is it applicable on?
They must carry out the conformity assessment procedure and ensure packaging complies with sustainability requirements.
Importers must ensure that packaging from a third country complies with all requirements before placing it on the market.
Any manufacturer, importer, or distributor established in an EU Member State who first makes packaging available on the EU market is considered the producer and is responsible for the waste management obligations such as EPR.
A producer established in a third country who makes packaging available directly to end users must appoint an authorized representative for the extended producer responsibility (EPR) in the Member State where the consumer is located.
Those operating in the HORECA (Hotels, Restaurants, and Catering/Cafés) sector must provide consumers with a system to bring their own containers or offer reusable packaging options.
Significance of EU-PPWR:
- Climate Neutrality: The PPWR contributes directly to the goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2050.
- Greenhouse Gas and Fossil Fuel Reduction: Applying the measures proposed in the EU-PPWR is expected to reduce Green House Gas (GHG) emissions from packaging to 430 lakh MT in 2030.
- Recyclable packaging: EU-PPWR establishes the core mandate that all packaging placed on the EU market must be designed to be fully recyclable by 2030.
New Rules introduced under EU-PPWR:
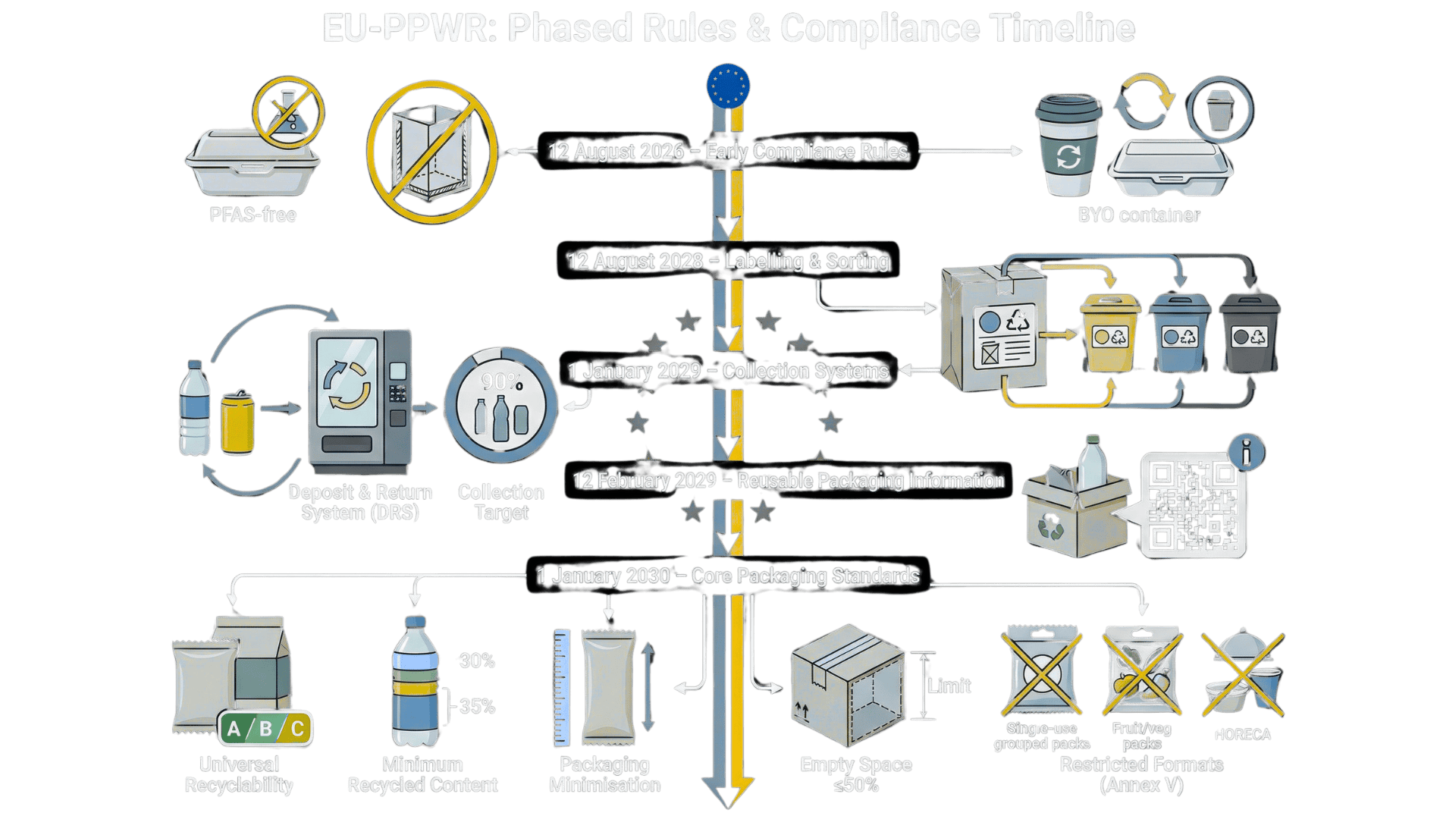
Various rules have been introduced under EU-PPWR which will be applicable in phased manner.
12 August 2026:
- PFAS Ban: Food contact packaging placed on the market is prohibited if it contains Per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS, or “forever chemicals”) above defined limit values.
- Ban on Excessive Packaging Design: Packaging with characteristics aiming only to increase the perceived volume of the product shall not be placed on the market.
- HORECA Refill Obligation: Final distributors in the HORECA sector making available beverages or prepared food for take away must provide a system for consumers to bring their own container to be filled, under conditions no less favorable than single-use options.
12 August 2028:
- Harmonized Sorting Label: Packaging placed on the market must be marked with a harmonized label detailing its material composition to facilitate sorting.
- Waste Receptacle Label: Member States must ensure that harmonized labels, corresponding to those on the packaging, are affixed to waste receptacles for collection of packaging waste.
1 January 2029:
- Deposit and Return Systems (DRS): Member States must establish DRS for single-use plastic beverage bottles and metal beverage containers
- 90% Collection Target: Member States must ensure the separate collection of at least 90% by weight of the single-use plastic beverage bottles and metal beverage containers placed on the market.
12 February 2029:
- QR Code on Reusable packaging: Reusable packaging placed on the market must bear a label informing users of its reusability, typically via a QR code or digital data carrier.
1 January 2030:
- Universal Recyclability: All packaging placed on the market must be recyclable (meeting recyclability performance grades A, B, or C).
- Minimum Recycled Content (Plastic): Plastic packaging must contain minimum percentages of recycled content recovered from post-consumer waste, including 30% for single-use plastic beverage bottles and 35% for other plastic packaging.
- Packaging Minimization: Manufacturers/importers must ensure packaging weight and volume is reduced to the minimum necessary to ensure functionality.
- Empty Space Restriction: Economic operators filling grouped, transport, or e-commerce packaging must ensure the maximum empty space ratio is 50%.
- Restrictions on Use: Ban on placing packaging on the market for formats listed in Annex V (e.g., single-use plastic grouped packaging; certain single-use fruit/veg packaging; single-use items for HORECA consumption within premises).
Targets set by European Union:
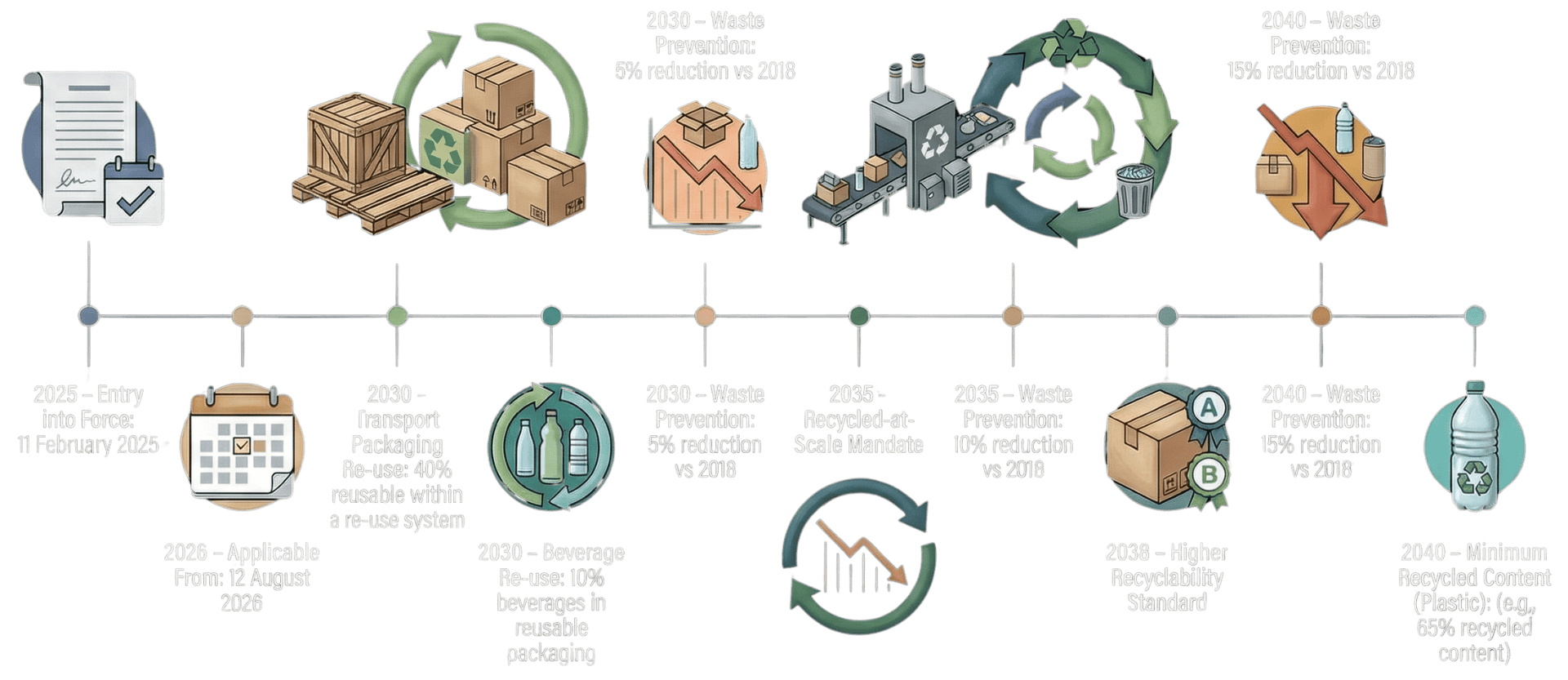
Final distributors must ensure at least 10% of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages are made available in reusable packaging within a re-use system (By January 2030).
Economic operators using specified transport and sales packaging formats must ensure at least 40% is reusable within a re-use system (By January 2030).
Member States must reduce the packaging waste generated per capita by at least 5% compared to 2018 levels (By January 2030).
Packaging must not only be designed to be recyclable but must also be proven to be effectively collected, sorted, and recycled at scale within established infrastructure (By 1 January 2035).
Member States must reduce the packaging waste generated per capita by at least 10% compared to 2018 levels (By 2035).
Packaging placed on the market must be recyclable within the higher performance grades of A or B (By 1 January 2038).
Member States must reduce the packaging waste generated per capita by at least 15% compared to 2018 levels (By 1 January 2040).
Plastic packaging must contain higher minimum recycled content (65%) (By 1 January 2040).

